On November 27, 2017, a final version of the new International Standards Organization (ISO) 45001 standard was published, creating an official ISO standard for occupational health and safety programs.
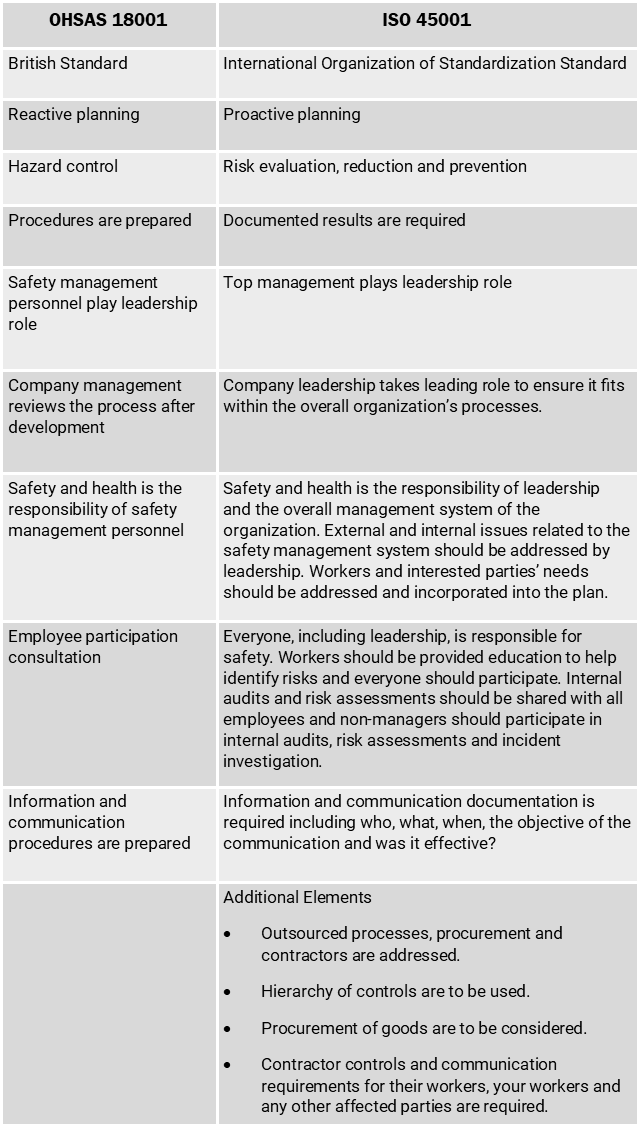
In the early 2000s there were international standards for environmental management systems with ISO 14001, but not health and safety. Thus, a British Standard was developed, called Occupational Health and Safety Assessment Series (OHSAS) 18001.
ISO 45001 takes much of what’s already in OHSAS 18001 and adds to it, reorganizes it to match current ISO formats, and modifies some areas. If you’re already OHSAS 18001 certified, you will have a good head start on ISO 45001 certification.
ISO 45001 brings the responsibility of safety to company leadership and establishes how safety incorporates into the entire organization, rather than making it a responsibility of safety management. The standard has more detailed clauses lining out its expectations of employee involvement, requiring the documentation of results and program effectiveness, risk evaluation and considering how safety affects all affected parties, not only employees but contractors, outsourced operations, vendors, etc.
Here are just a few of the differences between the two standards: