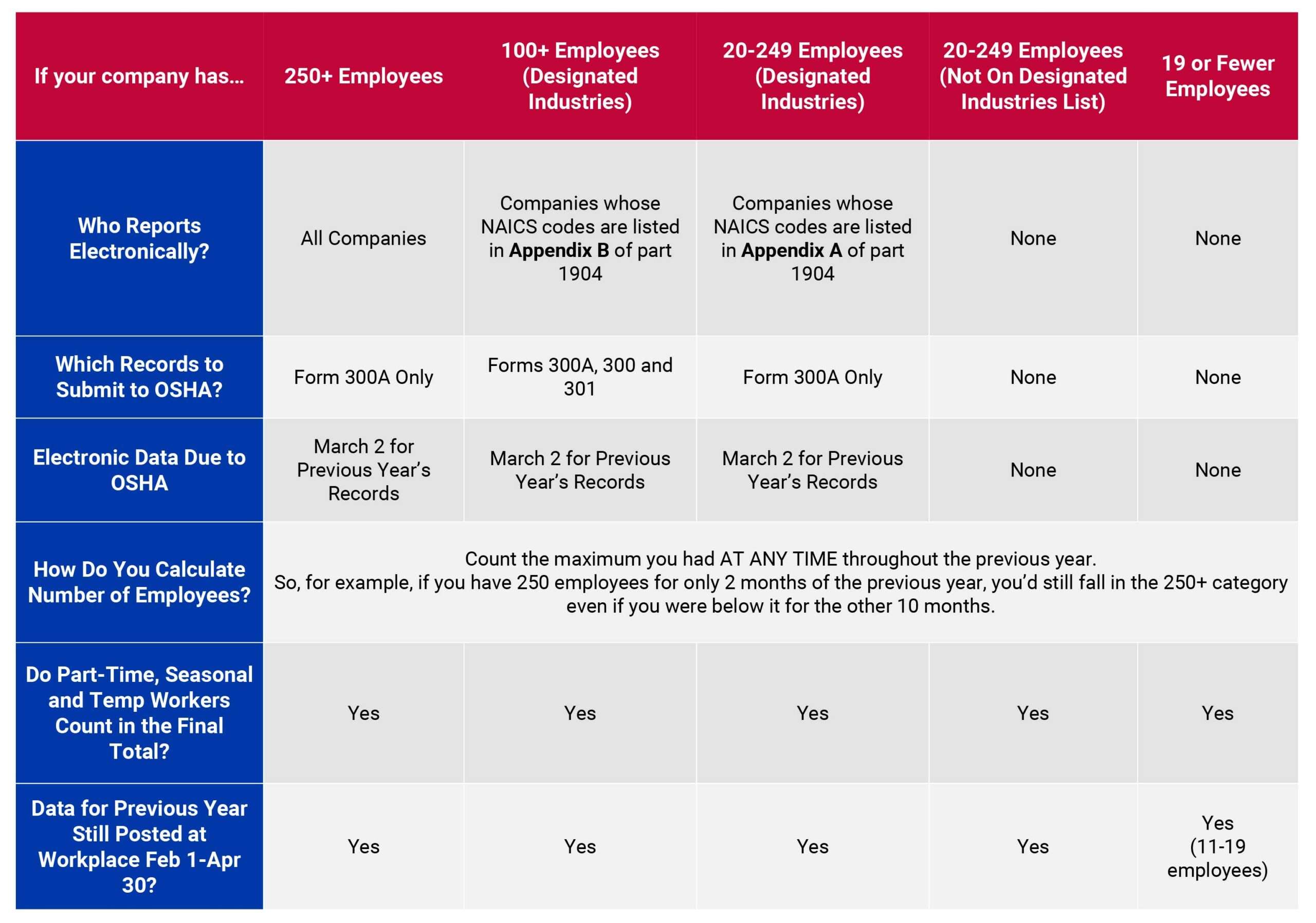
A Deeper Dive Into the “Haz” Words in OSHA, EPA and DOT and Where They Can Crossover
Every once in a while, we will get a call from someone looking for “Hazmat” training. To you, the word hazmat may mean one thing, but we guarantee to someone else it probably means something completely different.
iSi’s mission is to help companies navigate compliance with EPA, OSHA and DOT regulations. Once you start familiarizing yourself with those regulations, you will find that the definition of hazmat can be different for different agencies and different situations. You will also see that there are a number of words that include “haz” that can creep into the picture and be used interchangeably. An even deeper dive will show that each agency will either make up their own definition or borrow from one another.
Each Agency Has Its Own Focus
Regulations and their definitions are typically written in the perspective of the focus of the agency. Each agency has its own role to play in the workplace and how they use their haz words will often be reflective of that.
- OSHA – OSHA’s focus is safe and healthful working conditions for workers
- EPA – EPA’s focus is on human health and the condition of the environment
- DOT – DOT’s focus is on the safe, efficient, sustainable and equitable movement of people and goods
Once you know the perspective for each, that will help you be able to better understand regulations when they crossover or refer to one another.
Hazmat
Hazmat is a shortened version of “hazardous materials.” Each agency refers to hazardous materials a little differently.
In OSHA, the term hazmat can refer to hazardous materials or hazmat teams. OSHA says a hazardous material is something that can be a health hazard or a physical hazard. However, a hazmat team is an organized group of employees who perform work to handle and control spills or leaks of hazardous substances. Individually trained members of the hazmat team are called hazardous materials technicians. Later we’ll look at the OSHA HAZWOPER standard where many of these definitions are found.
To DOT, hazmat means “a substance or material capable of posing an unreasonable risk to health, safety, and property when transported in commerce…” It also can include hazardous substances, hazardous wastes, marine pollutants, elevated temperature materials, materials listed in the Hazardous Materials Table, and materials meeting their criteria for hazard classes and divisions. The term Hazmat employee in the regulations are those persons who package or prepare, physically transport, load, unload, design or makes packages for, fills out paperwork for or ensures the safe transportation of hazardous materials.
To EPA, a hazardous material is any item or chemical which can cause harm to people, plants, or animals when released by spilling, leaking, pumping, pouring, emitting, emptying, discharging, injecting, escaping, leaching, dumping or disposing into the environment.
From the definitions, you can see that OSHA was focused on people, DOT was focused on transportation and EPA was focused on the environment.
HazCom
Another shortened haz word is HazCom. This is short for the OSHA Hazard Communication Standard. This standard is all about hazardous chemicals, that is, any chemicals that are a physical or health hazard. The HazCom Standard deals with Safety Data Sheets (SDS), labeling, markings, training and more.
EPA’s Emergency Planning and Community Right to Know Act, or EPCRA, regulations refer to OSHA’s hazardous chemicals when it comes to which chemicals apply to the EPCRA regulation. Those which fall under the HazCom standard and have SDSs associated with them are included in EPCRA reporting requirements. Some companies also refer to HazCom training by the term Employee Right to Know training.
Hazardous Waste
Another haz is hazardous waste. The term hazardous waste comes from EPA’s Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) hazardous waste regulations. There’s a lengthy determination process one must go through to even determine if something can be defined to be a hazardous waste. You’ll see all of those criteria and the roadmap in the definition of hazardous waste at 40 CFR 261.2.
EPA’s website says, “Simply defined, a hazardous waste is a waste with properties that make it dangerous or capable of having a harmful effect on human health or the environment. Hazardous waste is generated from many sources, ranging from industrial manufacturing process wastes to batteries and may come in many forms, including liquids, solids gases, and sludges.”
Hazardous waste must be discarded and must be a solid waste. To be a solid waste, it must be a material that has been abandoned, recycled, is inherently waste-like or is a military munition.
Once you determine that it’s discarded and a solid waste, there are another set of questions to ask to make the determination if a waste is hazardous or not. This process is quite important and is required to be completed and documented for each of your wastes.
OSHA mentions hazardous waste in their HAZWOPER standard, calling hazardous waste anything that’s found to be a hazardous waste by the EPA definition or anything that DOT calls a hazardous waste in their definition.
In DOT regulations, DOT says hazardous waste is defined under EPA’s definition and that to ship hazardous waste a hazardous waste manifest is required. Hazardous waste is a hazardous material that is regulated for transportation. So when a vendor comes to pick up your hazardous waste, your company is the one technically shipping it and are therefore subject to all of the DOT hazmat regulations the same as if you were shipping any other hazardous material.
Hazardous Substances
All 3 agencies use the term hazardous substance.
In EPA, a hazardous substance is “Any substance, other than oil, which, when discharged in any quantities into waters of the U.S., presents an imminent and substantial danger to the public health or welfare, including but not limited to fish, shellfish, wildlife, shorelines and beaches (Section 311 of the Clean Water Act); identified by EPA as the pollutants listed under 40 CFR Part 116.” Hazardous substances are referred to in the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act (CERCLA, aka Superfund), the Clean Water Act (CWA), the Clean Air Act (CAA), the RCRA hazardous waste regulations, and the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA).
OSHA makes it easy. They say a hazardous substance is whatever EPA CERCLA says it is, whatever DOT says are hazardous materials, whatever EPA says a hazardous waste is, or any other biological or disease-causing agent that could lead to things like death, disease, behavioral abnormalities, cancer, genetic mutation, physiological malfunctions or physical deformations in such persons or their offspring.
DOT says a hazardous substance is a hazardous material when that material is listed in their Appendix A and when its single package exceeds the reportable quantity listed in the Appendix. They also have other considerations if it’s a mixture or solution or a radionuclide.
HAZWOPER
And finally, there’s HAZWOPER. Although it’s one of our more popularly discussed haz words, we left this for the end because this regulation actually uses all of the haz words in one place and seems to be one standard that incorporates so many different requirements from all 3 agencies within it.
HAZWOPER stands for Hazardous Waste Operations and Emergency Response. HAZWOPER is found in the 1910 General Industry Standards under Subpart H, Hazardous Materials. An identical copy can be found under a different subpart in the 1926 Construction Standards.
There are 3 main pieces or goals to HAZWOPER:
- Rules for conducting cleanup operations at sites determined to be EPA RCRA hazardous waste cleanup sites, cleanup operations at sites contaminated by hazardous substances on uncontrolled hazardous waste sites that EPA or another government agency have required to be cleaned up, or conducting voluntary cleanups at those same types of uncontrolled waste sites;
- Operations at treatment, storage and disposal facilities (TSD) regulated by EPA RCRA; and,
- Emergency response to releases of hazardous substances at any facility, any location.
Being an OSHA regulation, HAZWOPER is all about protecting the worker and the public during the cleanup, so all the guidance centers around preparing for and safely cleaning up hazardous substances.
The regulation mentions the term Hazmat teams in relation to those responding to the emergency responses found in part 3 of the standard.
HAZWOPER says any materials cleaned up and containerized into drums must meet appropriate regulatory requirements for DOT transportation, RCRA hazardous waste and OSHA safety regulations. Waste must be transported per DOT regulations while self-contained breathing apparatuses used by workers to protect themselves during work are to comply with DOT standards.
The DOT’s Emergency Response Guidebook is mentioned and often consulted for emergency response information and guidance.
If a company has prepared a contingency plan per EPA requirements and that plan includes emergency response information, the company can use that contingency plan as part of its emergency response plan so that efforts are not duplicated.
On the EPA side, because OSHA regulations don’t apply to local and state governments, EPA has adopted the HAZWOPER standard into 40 CFR 311 to apply to those local and state governments and any of those not covered by a state OSHA-approved plan.
Also in EPA, emergency spills trigger a whole host of reporting requirements as well as emergency response plans and training to protect the environment from hazardous waste spills, oil spills, pipeline leaks and chemical releases to water, air or land.
Conclusion
This is not an exhaustive list of haz references or examples where all 3 agencies cross over, but hopefully it gave you an idea of how these terms and the rules related to them can be so different in some cases, but so intertwined in others. The haz words used can differ depending on the situation.
So, if you call us asking for hazmat training, you’re likely to get a lot of questions from us about your end goal.
What haz words have you come across? What examples did we miss? We’ll be posting this on our Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter and Instagram pages. We’d love to hear from you!






 Grill outside, away from structures. Make sure your grill is stable on a flat surface so that it can’t be tipped over. Keep the grill clean and wait for it to cool before you clean it. Check for propane leaks on your gas grill, and if you’re using charcoal, wait for the coals to completely cool before you dispose of them. Always dispose coals into a metal container. If the flame goes out on your grill, turn off the grill AND turn off the gas, then wait 5 min. before relighting. If you use a charcoal grill, only use charcoal starter fluid. If the fire starts to go out, don’t add any starter fluid or any other flammable liquids to the fire.
Grill outside, away from structures. Make sure your grill is stable on a flat surface so that it can’t be tipped over. Keep the grill clean and wait for it to cool before you clean it. Check for propane leaks on your gas grill, and if you’re using charcoal, wait for the coals to completely cool before you dispose of them. Always dispose coals into a metal container. If the flame goes out on your grill, turn off the grill AND turn off the gas, then wait 5 min. before relighting. If you use a charcoal grill, only use charcoal starter fluid. If the fire starts to go out, don’t add any starter fluid or any other flammable liquids to the fire. For walk-behind mowers, rotary blades underneath the mower can rotate at 200 mph. Keep your hands and feet away from the blade area when it’s running. Never remove installed safety guards such as directional flaps or shielded discharge outlets or bypass safety shut down devices such as clutch handles or switches that stop the blade as soon as you let go. Mow back and forth along the side of a steep hill, never up and down the slope.
For walk-behind mowers, rotary blades underneath the mower can rotate at 200 mph. Keep your hands and feet away from the blade area when it’s running. Never remove installed safety guards such as directional flaps or shielded discharge outlets or bypass safety shut down devices such as clutch handles or switches that stop the blade as soon as you let go. Mow back and forth along the side of a steep hill, never up and down the slope. to cool. Keep people and pets at least 60 ft. away and stop if you’re approached. Use both hands when operating.
to cool. Keep people and pets at least 60 ft. away and stop if you’re approached. Use both hands when operating. Get familiar with the difference between these plants and how to spot them. Remember, leaves of three, let them be! For rashes use a cold compress, calamine lotion, non-prescription hydrocortisone cream, or an antihistamine to ease itching. You can also use other non-traditional treatments such as wrap dipped in apple cider vinegar. Call your doctor if the rash is near your eyes or covers a large part of your body.
Get familiar with the difference between these plants and how to spot them. Remember, leaves of three, let them be! For rashes use a cold compress, calamine lotion, non-prescription hydrocortisone cream, or an antihistamine to ease itching. You can also use other non-traditional treatments such as wrap dipped in apple cider vinegar. Call your doctor if the rash is near your eyes or covers a large part of your body. Never swim alone, and always supervise children. Open water prevents a number of different hazards that pools don’t. These include limited visibility, depth changes, uneven surfaces, unknown objects that can be stepped on, and currents and undertow. Enter the water feet first to prevent head injury. This includes using water slides. Never dive into water that’s less than 8 ft. deep. Be on the lookout for maintenance issues around the swim area. Be alert of wet floors, sharp edges, broken glass, exposed bolts, broken ladders, broken railings and clear markings of water depth. If you find yourself struggling or accidentally fall in, float to live. Try not to panic as calmness will save you. Lean back and use your arms and legs to keep you afloat with gentle movements. Once you’re calm your breathing is controlled, then call for help or swim to safety. Don’t let your dog swim without supervision. While many dogs know how to swim, some can easily tire out.
Never swim alone, and always supervise children. Open water prevents a number of different hazards that pools don’t. These include limited visibility, depth changes, uneven surfaces, unknown objects that can be stepped on, and currents and undertow. Enter the water feet first to prevent head injury. This includes using water slides. Never dive into water that’s less than 8 ft. deep. Be on the lookout for maintenance issues around the swim area. Be alert of wet floors, sharp edges, broken glass, exposed bolts, broken ladders, broken railings and clear markings of water depth. If you find yourself struggling or accidentally fall in, float to live. Try not to panic as calmness will save you. Lean back and use your arms and legs to keep you afloat with gentle movements. Once you’re calm your breathing is controlled, then call for help or swim to safety. Don’t let your dog swim without supervision. While many dogs know how to swim, some can easily tire out. g and damage your vehicle’s suspension. Check the hitch for the maximum trailer and maximum tongue weights it can safely support. Make sure you have the proper hitch ball for the trailer. Incorrectly sized hitch balls are the #1 cause of trailer accidents. When hauling loads, 60% of the load on the trailer should be placed on the front half of the trailer, with a tongue weight of 10-15% of the total weight that’s loaded on the trailer. Ensure weight is evenly distributed on the left and right sides of the trailer. Straps are critical — broken or cheap straps can fail fast. Use ratchet straps for anything heavier than an average person and use more than one strap in case one comes loose. The working load of the strap should be more than the weight of what you’re hauling. Check your tires on both the vehicle and the trailer and make sure your lights work before you leave. Take spare bulbs and fuses with you. Check your brakes and make sure the breakaway cable is properly attached to your tow vehicle. Carry spare parts such as at least one trailer spare tire as well as extra wheel bearings and hubs.
g and damage your vehicle’s suspension. Check the hitch for the maximum trailer and maximum tongue weights it can safely support. Make sure you have the proper hitch ball for the trailer. Incorrectly sized hitch balls are the #1 cause of trailer accidents. When hauling loads, 60% of the load on the trailer should be placed on the front half of the trailer, with a tongue weight of 10-15% of the total weight that’s loaded on the trailer. Ensure weight is evenly distributed on the left and right sides of the trailer. Straps are critical — broken or cheap straps can fail fast. Use ratchet straps for anything heavier than an average person and use more than one strap in case one comes loose. The working load of the strap should be more than the weight of what you’re hauling. Check your tires on both the vehicle and the trailer and make sure your lights work before you leave. Take spare bulbs and fuses with you. Check your brakes and make sure the breakaway cable is properly attached to your tow vehicle. Carry spare parts such as at least one trailer spare tire as well as extra wheel bearings and hubs. signaling devices, emergency supplies and a first aid kit. Think about your footing and be alert to slippery areas. Watch for low hanging branches and take extra caution near cliffs, outcroppings, hills, and water edges. No matter how clear a stream looks, it’s likely to contain waterborne parasites & microorganisms, so pack your own water. Make sure your fires are always attended, cannot be spread laterally or vertically (used a grill or stone surface) and drown it with water to put it out. Embers buried deep in the pile can reignite later. Be cautious when using a propane stove. Tents should be flame retardant and far enough away from the campfire. Wear sunscreen, hats, sunglasses and drink plenty of water. Pack carbohydrate-energy bars, granola candy or fruit for instant energy on your hikes.
signaling devices, emergency supplies and a first aid kit. Think about your footing and be alert to slippery areas. Watch for low hanging branches and take extra caution near cliffs, outcroppings, hills, and water edges. No matter how clear a stream looks, it’s likely to contain waterborne parasites & microorganisms, so pack your own water. Make sure your fires are always attended, cannot be spread laterally or vertically (used a grill or stone surface) and drown it with water to put it out. Embers buried deep in the pile can reignite later. Be cautious when using a propane stove. Tents should be flame retardant and far enough away from the campfire. Wear sunscreen, hats, sunglasses and drink plenty of water. Pack carbohydrate-energy bars, granola candy or fruit for instant energy on your hikes.